Connected cars represent a significant advancement in automotive technology, leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) integration to enhance vehicle capabilities, safety, and convenience. This article explores the concept of connected cars, their IoT components, benefits, challenges, and the future of remote vehicle management.

Understanding Connected Cars:
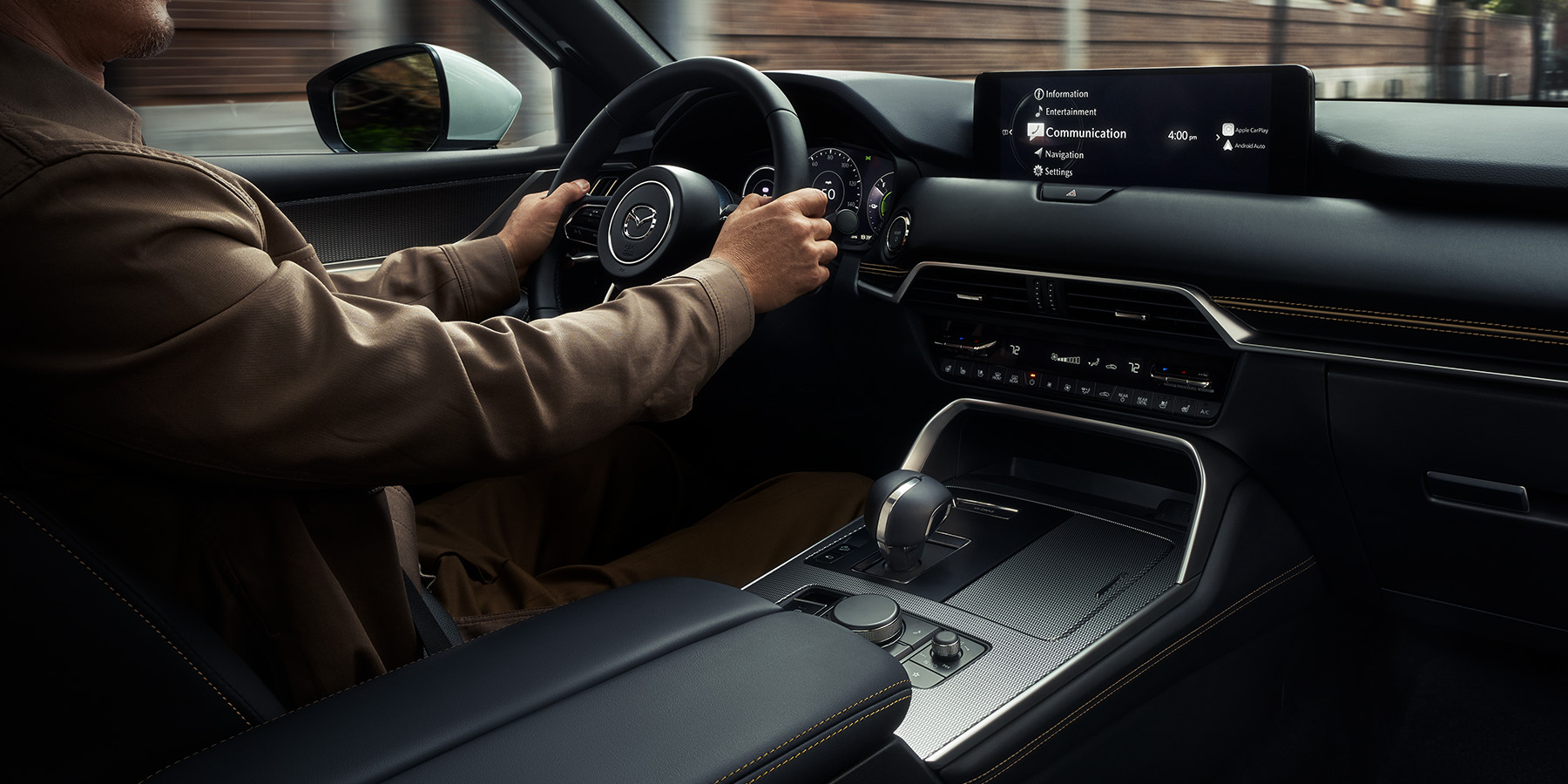
Connected cars are vehicles equipped with internet connectivity and integrated sensors, allowing them to communicate with external networks, other vehicles, and smart devices. This connectivity enables a wide range of functionalities beyond traditional transportation, transforming the driving experience through real-time data exchange and remote control capabilities.
IoT Components in Connected Cars:
- Telematics Control Unit (TCU): The TCU serves as the gateway for vehicle connectivity, facilitating communication between the car’s systems and external networks via cellular or satellite networks. It collects and transmits data on vehicle performance, location, maintenance status, and driver behavior.
- Embedded Connectivity: Embedded SIM cards or eSIMs enable seamless connectivity for transmitting and receiving data, ensuring continuous communication between the vehicle and IoT platforms without relying on external devices.
- Sensors and Data Collection: Connected cars are equipped with various sensors (e.g., GPS, radar, cameras) that gather real-time data on road conditions, traffic patterns, environmental factors, and vehicle health metrics. This data is crucial for optimizing performance, enhancing safety, and enabling predictive maintenance.
Benefits of Connected Cars:
- Enhanced Safety and Security: Connected cars leverage IoT to offer advanced safety features such as automatic emergency braking, collision avoidance systems, and real-time traffic alerts. Remote monitoring and tracking capabilities enhance vehicle security, enabling owners to locate stolen vehicles and remotely disable them if necessary.
- Remote Vehicle Management: IoT integration enables remote access to vehicle functions via smartphone apps or web portals. Owners can remotely lock/unlock doors, start the engine, adjust climate controls, and monitor fuel levels, enhancing convenience and user control.
- Predictive Maintenance: Connected cars use IoT data analytics to monitor vehicle performance metrics and predict potential maintenance issues before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces downtime, prevents costly repairs, and extends the lifespan of vehicle components.
- Personalized Driving Experience: Connected cars offer personalized features such as customized infotainment preferences, navigation routes based on real-time traffic data, and adaptive cruise control settings tailored to individual driving habits.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Cybersecurity Risks: The connectivity of connected cars exposes them to cybersecurity threats such as hacking, data breaches, and remote hijacking. Automakers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive vehicle data and ensure passenger safety.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The collection and transmission of personal and vehicle data raise privacy concerns among consumers. Clear data governance policies, transparent data usage practices, and user consent mechanisms are essential to addressing privacy issues.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Reliable network coverage and infrastructure are crucial for seamless connectivity and real-time data exchange. Rural areas or regions with poor network coverage may experience limitations in accessing connected car services.
Future Trends in Remote Vehicle Management:
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance connectivity speed, bandwidth, and reliability, enabling faster data transmission, low-latency communication, and support for bandwidth-intensive applications in connected cars.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing technology will process data closer to the source (i.e., within the vehicle or nearby edge servers), reducing latency and improving response times for real-time applications such as autonomous driving and safety-critical systems.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI-powered algorithms will analyze vast amounts of IoT data to optimize vehicle performance, predict maintenance needs, and personalize driver experiences based on behavioral patterns and contextual data.
Conclusion:
Connected cars represent the future of automotive innovation, leveraging IoT integration and remote vehicle management capabilities to enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience.

As technology continues to evolve, connected cars will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of mobility, offering drivers personalized, connected, and intelligent transportation solutions. Embracing advancements in connectivity, cybersecurity, and data analytics will be key to unlocking the full potential of connected cars and delivering sustainable, efficient, and safe transportation solutions globally.